Adipokines In Inflammation And Metabolic Disease
Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Obesity increases the risk for metabolic cardiovascular chronic inflammatory and several malignant diseases and therefore may contribute to shortened lifespan. However the relationship between adipokine concentrations inflammation insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. Metabolic inflammation has been increasingly recognized as a unifying mechanism linking obesity to a broad spectrum of pathological conditions.
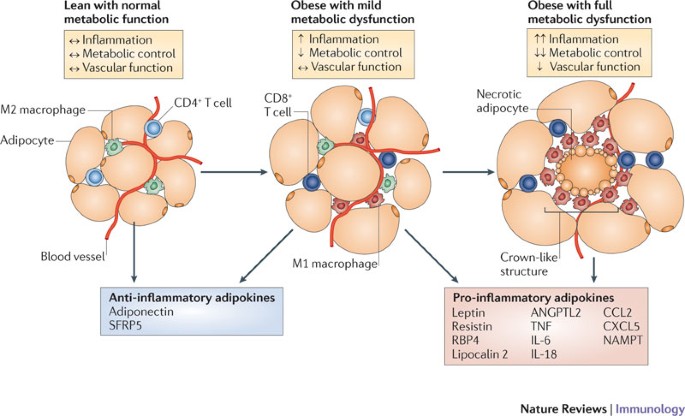
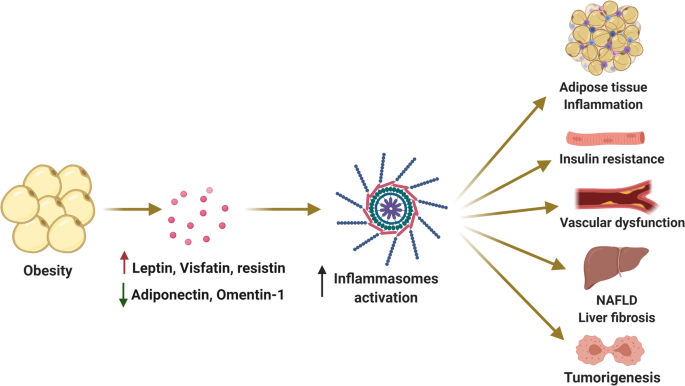
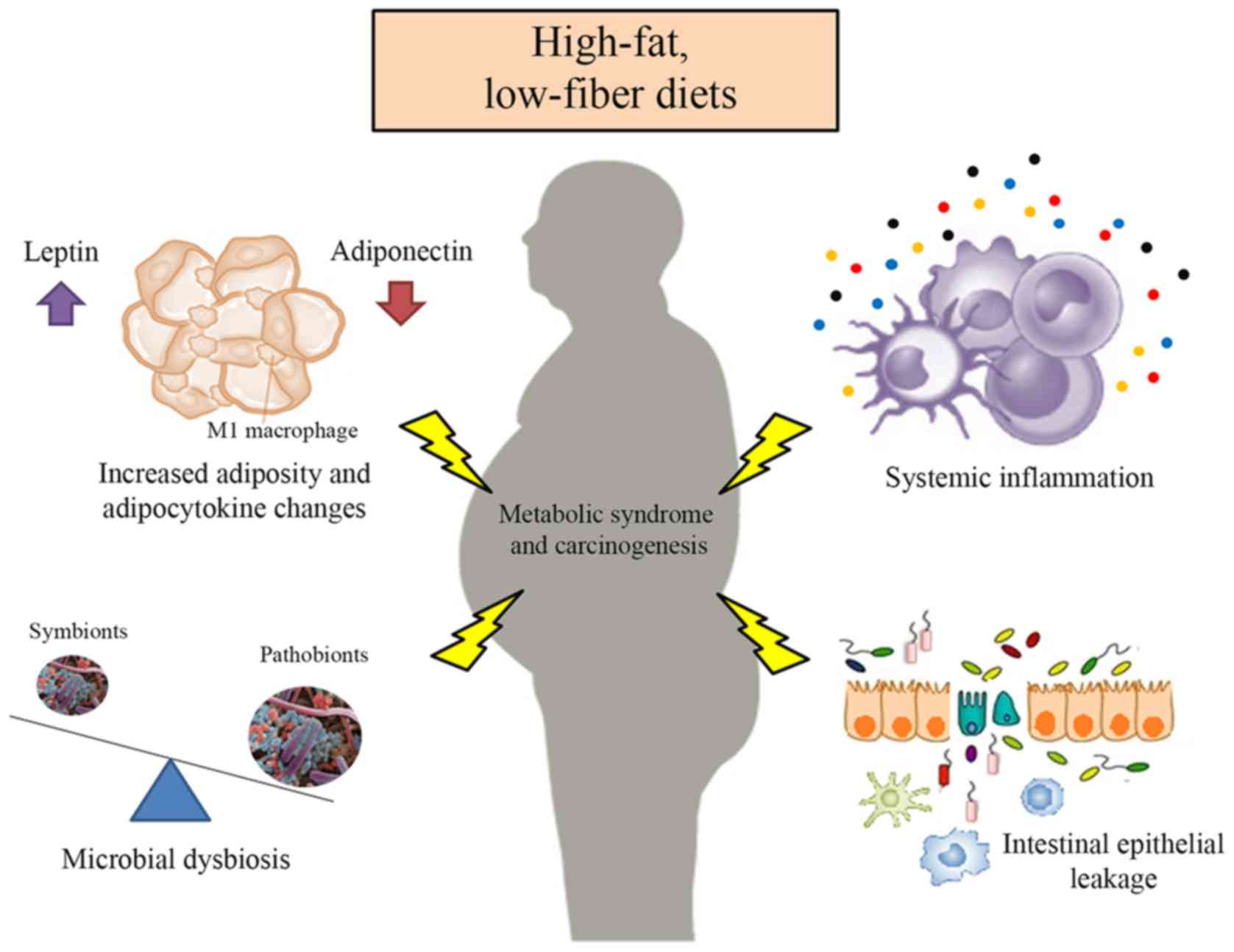
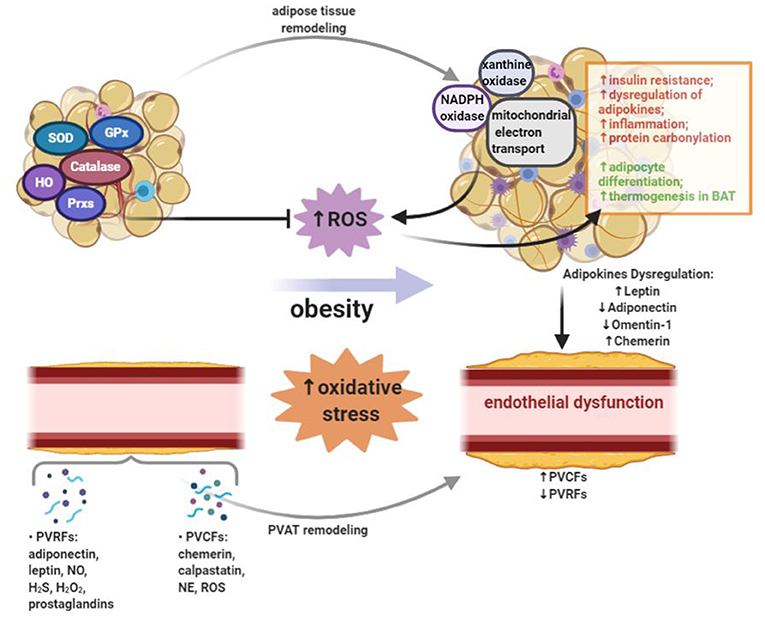
Abnormal adipocyte physiology leads to alterations in the secretory profile of these adipokines with detrimental consequences on local and peripheral glucose and lipid metabolism Figure 1. In addition obesity induces production of inflammatory cytokines often referred to together with adipokines as adipocytokines and infiltration of immune cells into adipose tissue which creates a state of chronic low-grade inflammation. Specifically digestive cancers grow anatomically near adipose.
The adipokines possess pro- and anti-inflammatory properties and play a critical role in integrating systemic metabolism with immune function. Protects against several metabolic and cardiovascular disorders that are associated with obesity. In calorie restriction and starvation proinflammatory adipokines decline and anti-inflammatory adipokines increase which informs the host of energy deficits and contributes to the suppression of immune function.
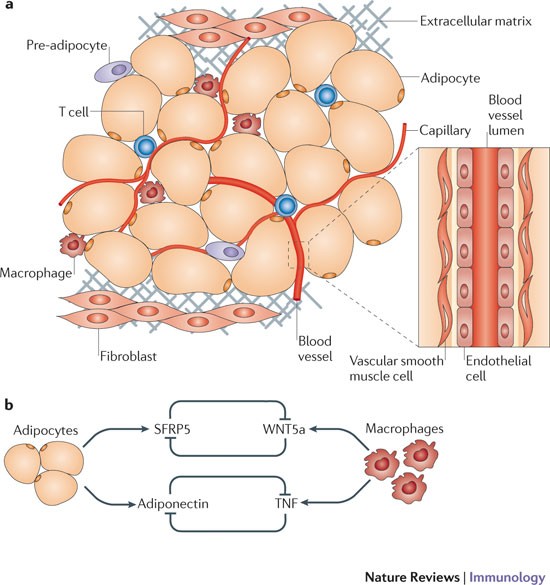
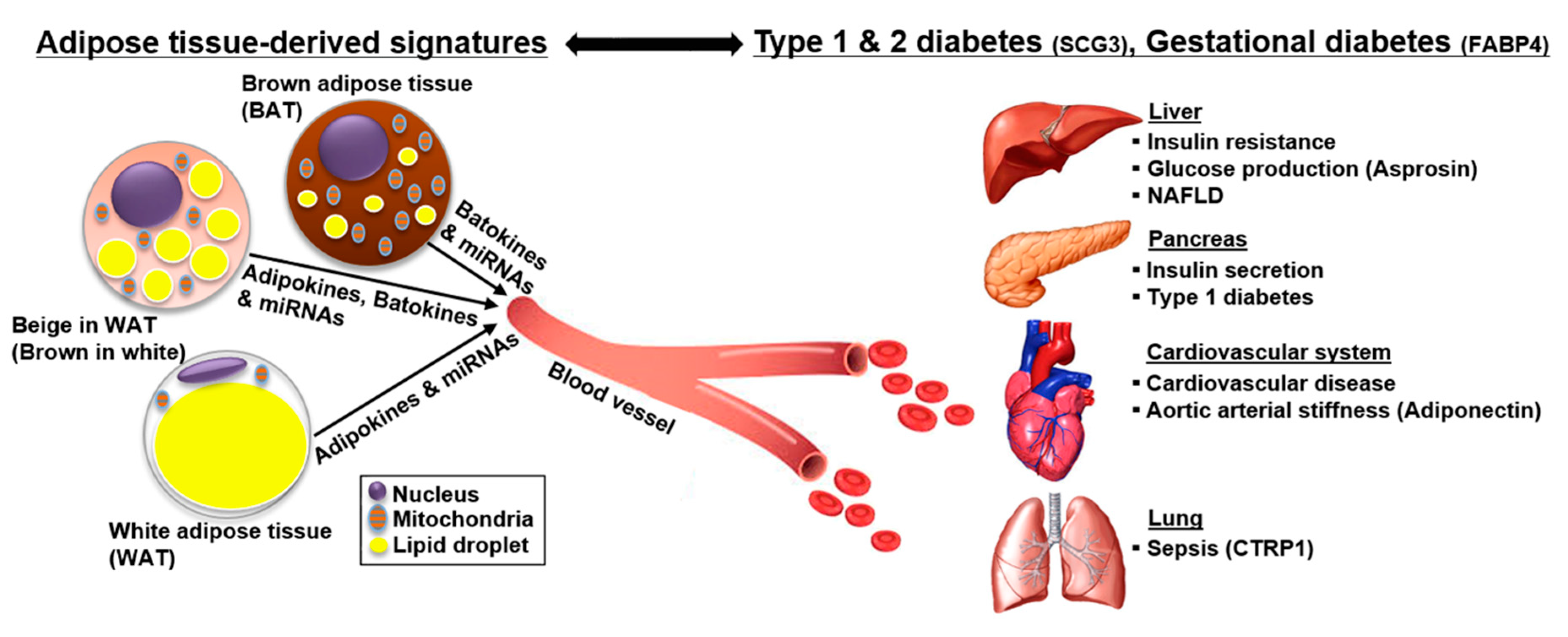
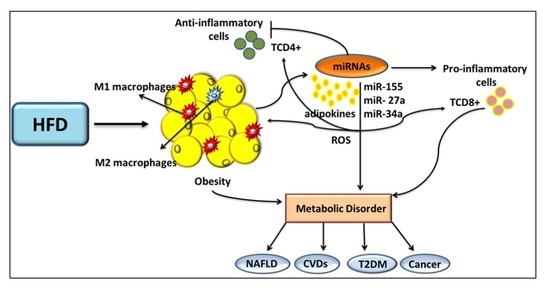
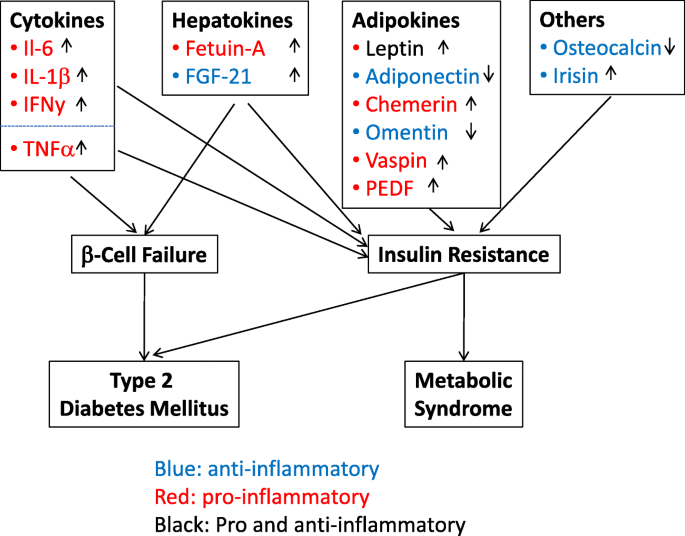
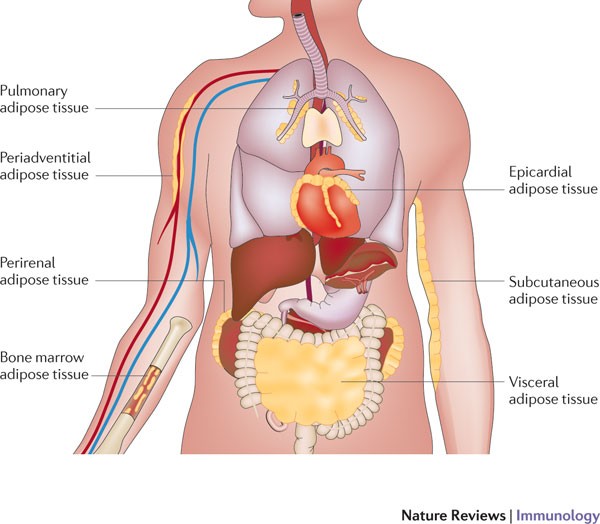
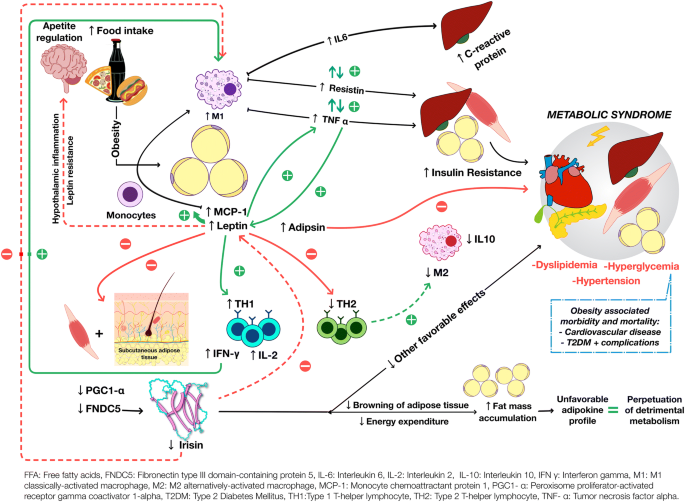
Research of the last years demonstrated a dysregulated adipokine balance as an important link between inflammation MetS and consequential disorders. Apart from the skin manifestations psoriasis is associated with the metabolic syndrome MetS known to increase the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disorders. Adipose tissue is a highly dynamic endocrine tissue and constitutes a central node in the interorgan crosstalk network through adipokines which cause pleiotropic effects including the modulation of angiogenesis metabolism and inflammation.
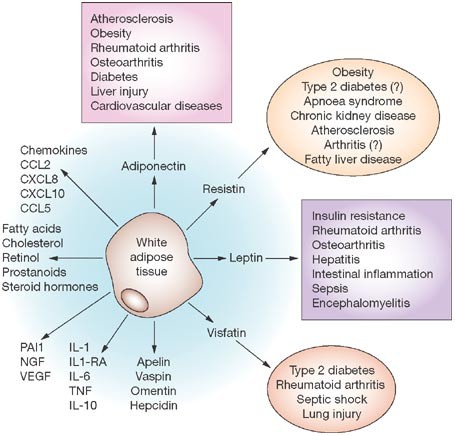
Adipose tissue functions as a key endocrine organ by releasing multiple bioactive substances known as adipose-derived secreted factors or adipokines that have pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory. Adipokines include adiponectin leptin resistin and some proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin IL-6. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Division of Infectious Diseases A2200-MCN 1161 21st Avenue South Nashville TN 37232.
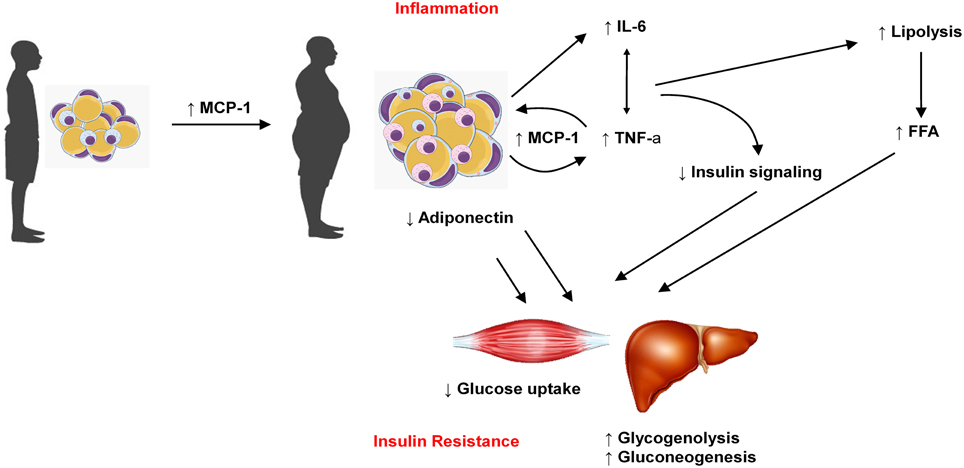
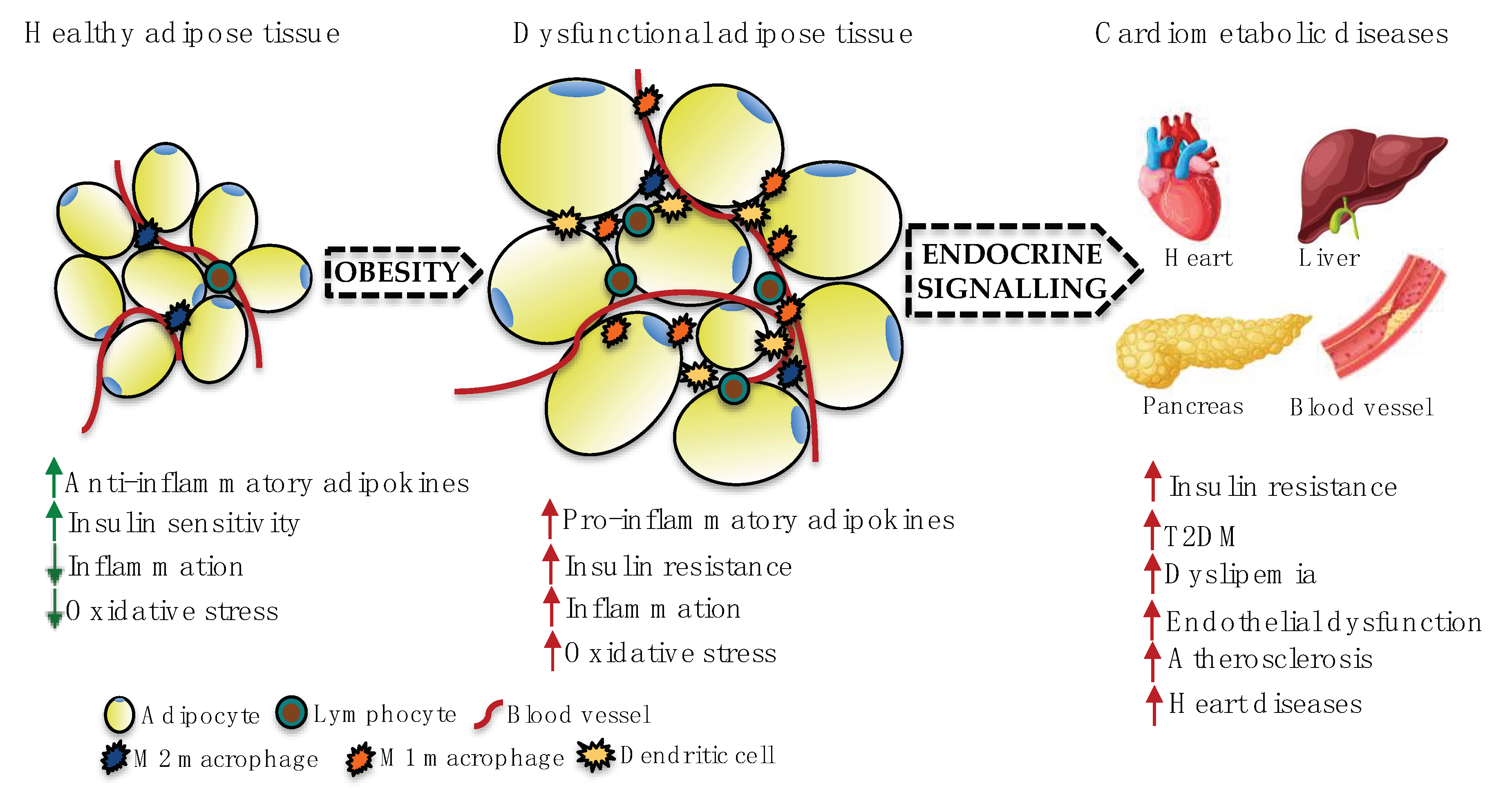
These results were surprising as most adipokines stimulate inflammatory responses are upregulated in obesity and promote obesity-induced metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Tissue have diverse endocrine and immunologic effects and circulating levels reflect adipocyte lipid content local inflammation. Accumulating evidence indicates that obesity causes chronic low-grade inflammation and that this contributes to systemic metabolic dysfunction that is associated with obesity-linked disorders.
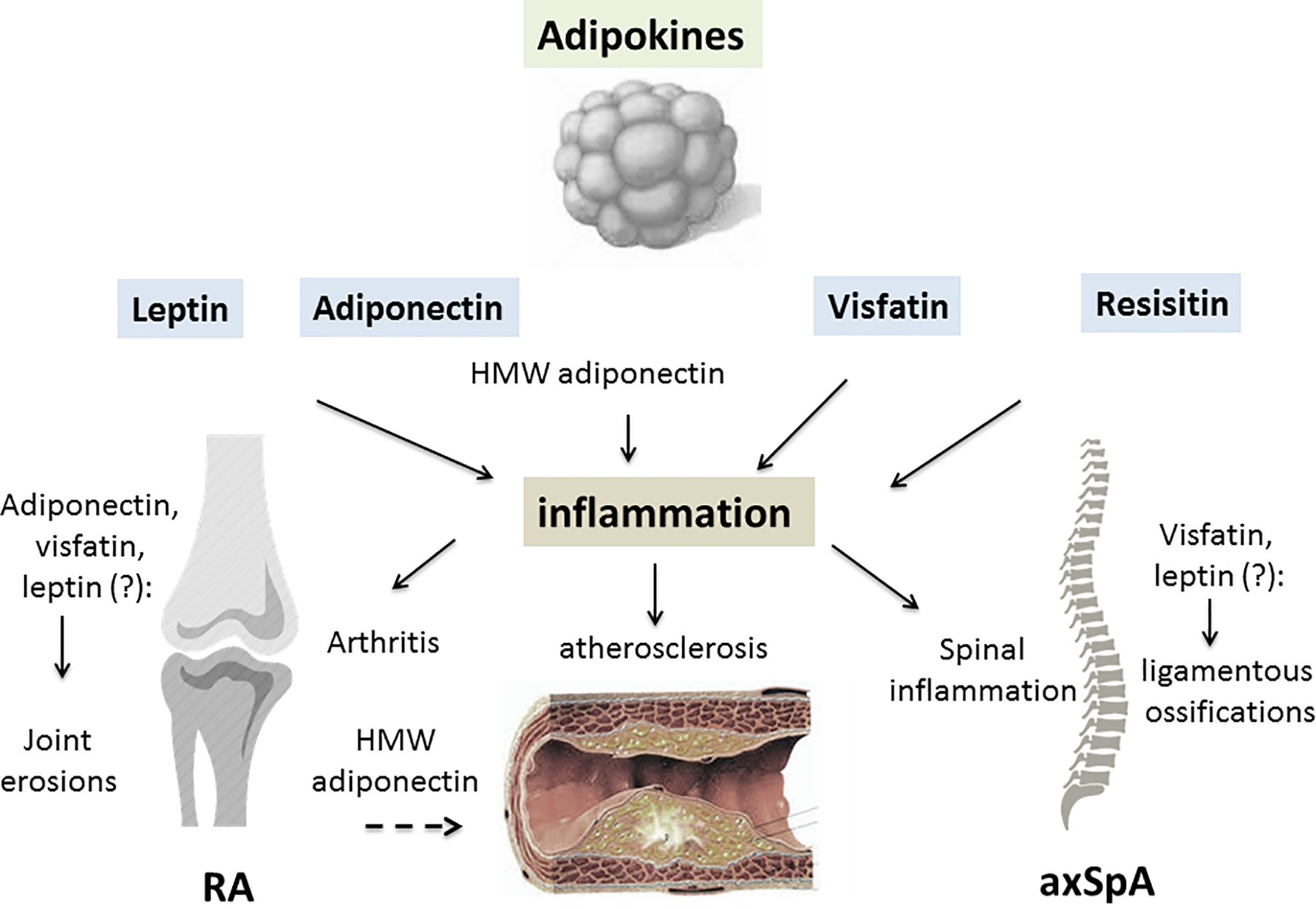
Obesity increases the risk for metabolic cardiovascular chronic inflammatory and several malignant diseases and therefore may contribute to shortened lifespan. Adipokines are pleiotropic molecules that contribute to the so-called low-grade inflammatory state of obese subjects creating a cluster of metabolic aberrations including autoimmune and inflammatory diseases that affect joints and bone 41.
Accumulating evidence indicates that obesity causes chronic low-grade inflammation and that this contributes to systemic metabolic dysfunction that is associated with obesity-linked disorders.
Adipokines include adiponectin leptin resistin and some proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin IL-6. To date the adipose tissue is considered as an endocrine organ able to mediate biological effects on metabolism and inflammation contributing to the maintenance of energy homeostasis and probably pathogenesis of obesity-related metabolic and inflammatory complications 8. Metabolic imbalance triggers systemic and central inflammation and induces excessive accumulation of adipose tissue involving increased secretion of adipokines 44. Adipokines include adiponectin leptin resistin and some proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin IL-6. In addition to leptin TNF and IL-6 more recently identified adipokines that promote inflammation include resistin retinol-binding protein 4 RbP4 lipocalin 2 IL-18 angiopoietin-like protein 2 ANGPTL2 CC-chemokine ligand 2 CCL2 CXC-chemokine ligand 5 CXCL5 and nicotinamide phospho ribosyltransferase NAmPT TABLE 1 and this subset of factors is discussed in more. Obesity increases the risk for metabolic cardiovascular chronic inflammatory and several malignant diseases and therefore may contribute to shortened lifespan. The adipokines possess pro- and anti-inflammatory properties and play a critical role in integrating systemic metabolism with immune function. Obesity increases the risk for metabolic cardiovascular chronic inflammatory and several malignant diseases and therefore may contribute to shortened lifespan. Adipokines are pleiotropic molecules that contribute to the so-called low-grade inflammatory state of obese subjects creating a cluster of metabolic aberrations including autoimmune and inflammatory diseases that affect joints and bone 41.
In addition obesity induces production of inflammatory cytokines often referred to together with adipokines as adipocytokines and infiltration of immune cells into adipose tissue which creates a state of chronic low-grade inflammation. Abnormal adipocyte physiology leads to alterations in the secretory profile of these adipokines with detrimental consequences on local and peripheral glucose and lipid metabolism Figure 1. Obesity increases the risk for metabolic cardiovascular chronic inflammatory and several malignant diseases and therefore may contribute to shortened lifespan. In addition obesity induces production of inflammatory cytokines often referred to together with adipokines as adipocytokines and infiltration of immune cells into adipose tissue which creates a state of chronic low-grade inflammation. Adipokines Weight Gain and Metabolic and Inflammatory Markers. Adipokines may serve as markers for the early diagnosis of metabolic cardiovascular inflammatory or malignant diseases. Protects against several metabolic and cardiovascular disorders that are associated with obesity.

































Post a Comment for "Adipokines In Inflammation And Metabolic Disease"