What Cells Are Damaged In Huntington's Disease
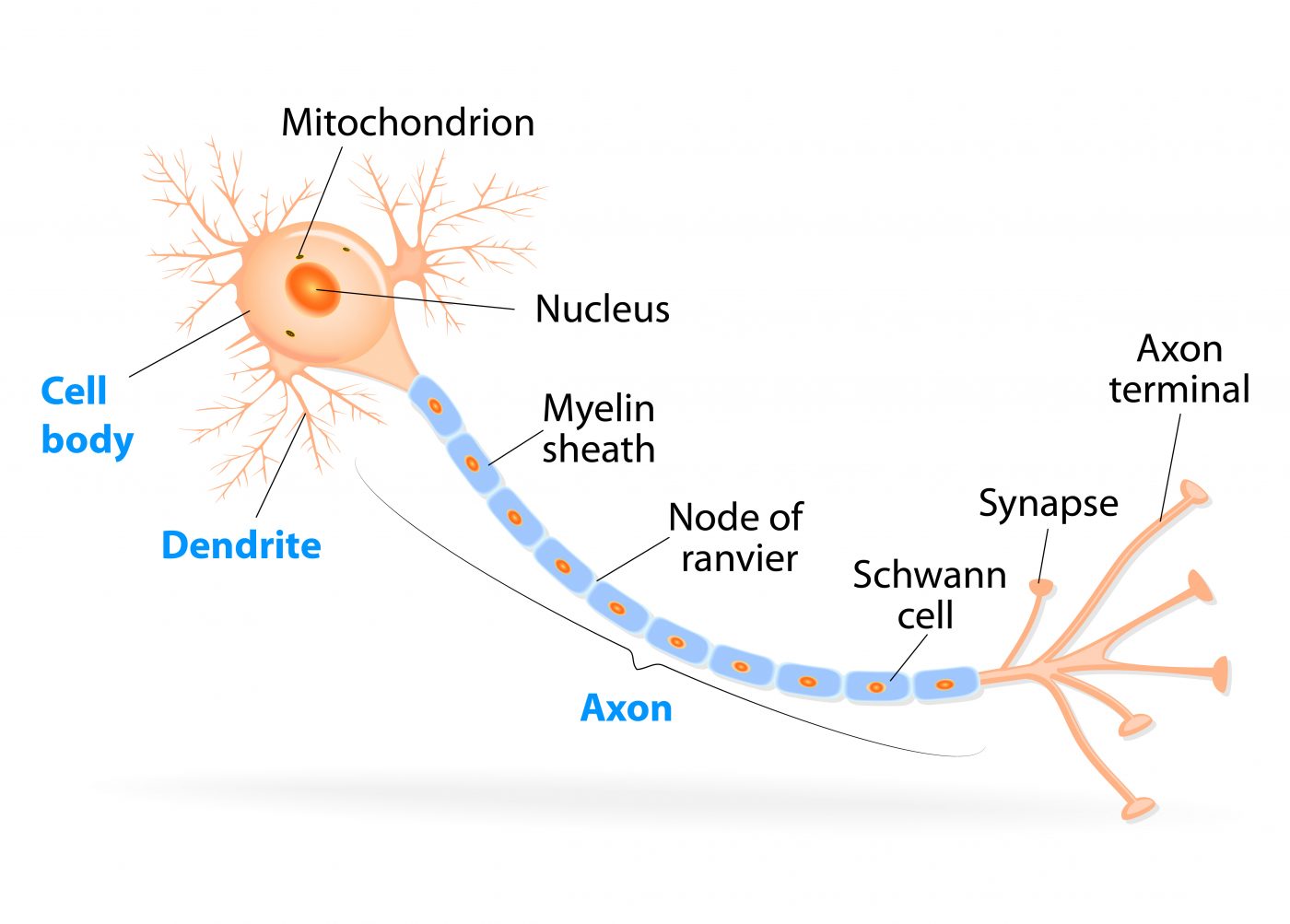
What cells are damaged in huntington's disease. Therapeutic approaches based on stem cells have received considerable attention as potential treatments for Huntingtons disease HD which is a fatal inherited neurodegenerative disorder caused by progressive loss of GABAergic medium spiny neurons MSNs in the striatum of the forebrain. MSNs receive and coordinate information from other neurons in the brain to control movement intellectual processes and emotion. What is Huntingtons disease.
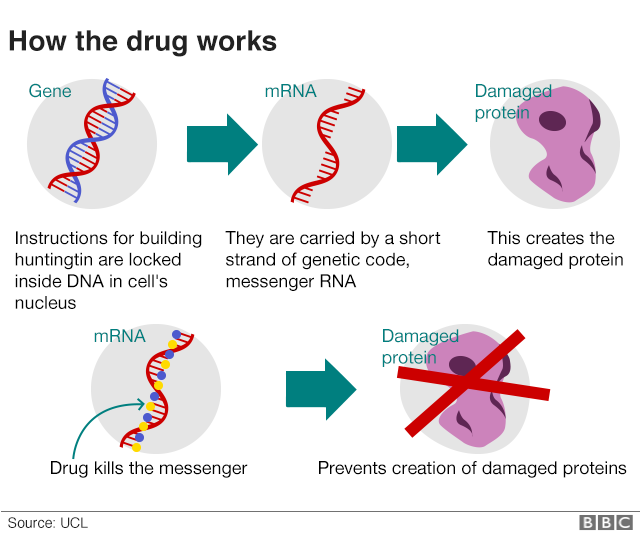
Nationwide an estimated 30000 people have Huntingtons disease. This section of the website gives an introduction to the brain focusing on the changes caused by HD. Huntingtons patients have an abnormal mutant version of a protein called huntingtin.
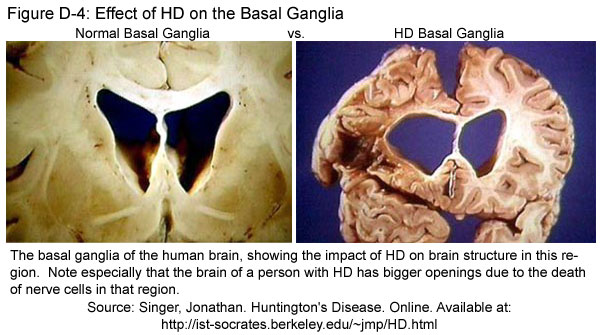
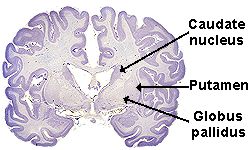
Huntingtons disease HD is an inherited disorder that causes nerve cells called neurons in parts of the brain to gradually break down and die. This brain damage gets progressively worse over time and can affect movement cognition perception awareness thinking judgement and behaviour. Huntington disease is caused by gradual degeneration of parts of the basal ganglia called the caudate nucleus and putamen.
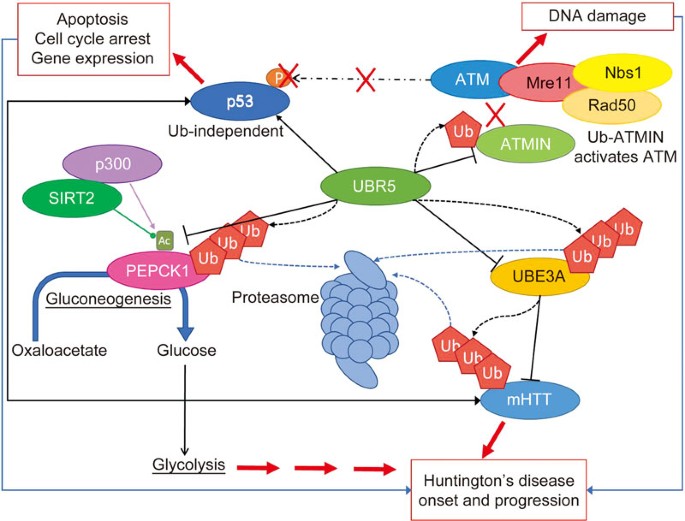
Huntingtons Disease HD mainly affects nerve cells in the brain called medium spiny neurons MSNs. An accumulation of DNA breakages is thought to contribute to the development of Huntingtons disease a devastating and currently incurable condition where brain cells slowly die. Though once considered a rare disease HD is one of the more frequently encountered hereditary diseases.
Locating the Basal Ganglia. They help smooth out and coordinate movements. People suffering from Huntingtons gradually lose both their mental and physical abilities and they usually die early.
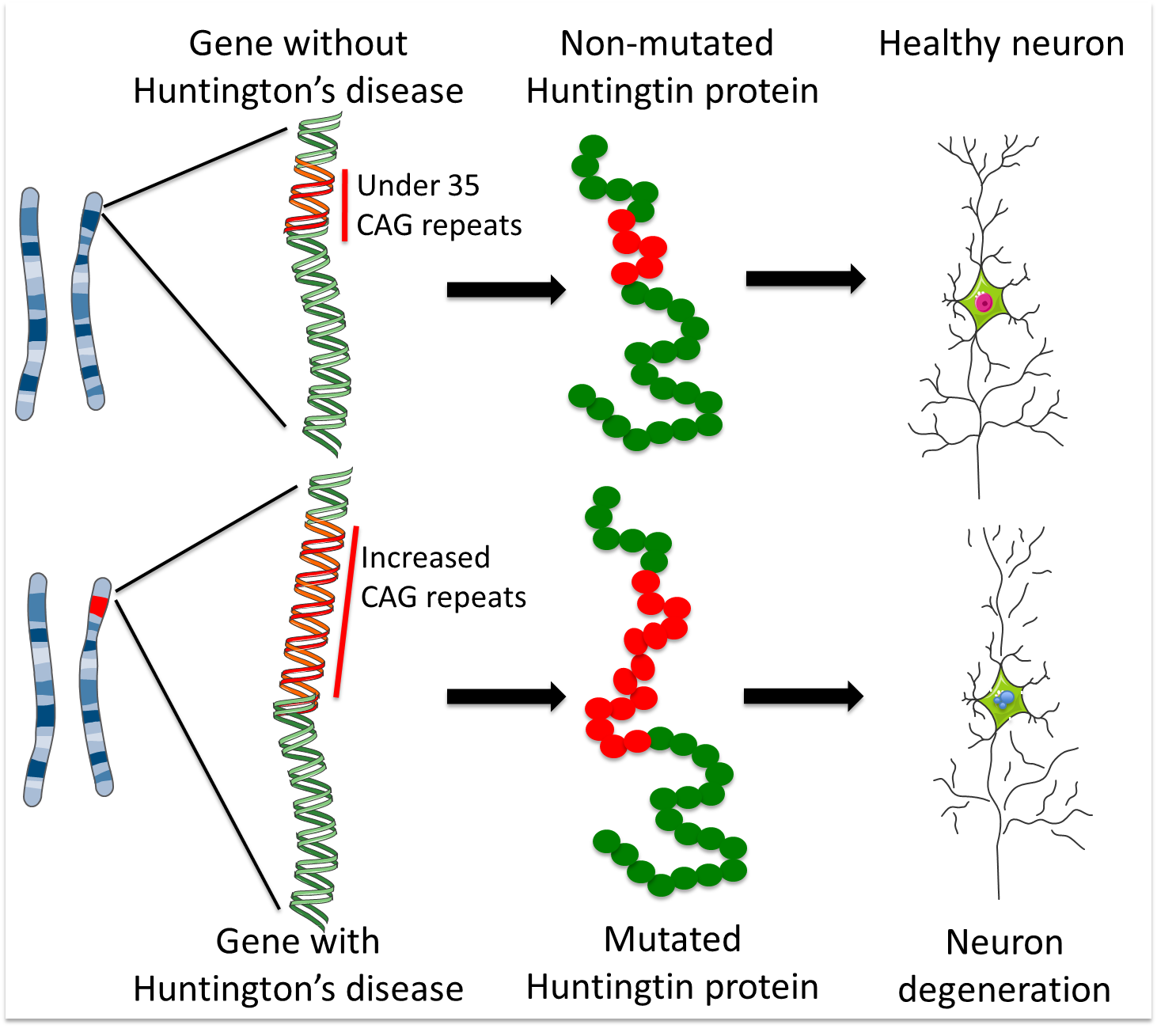
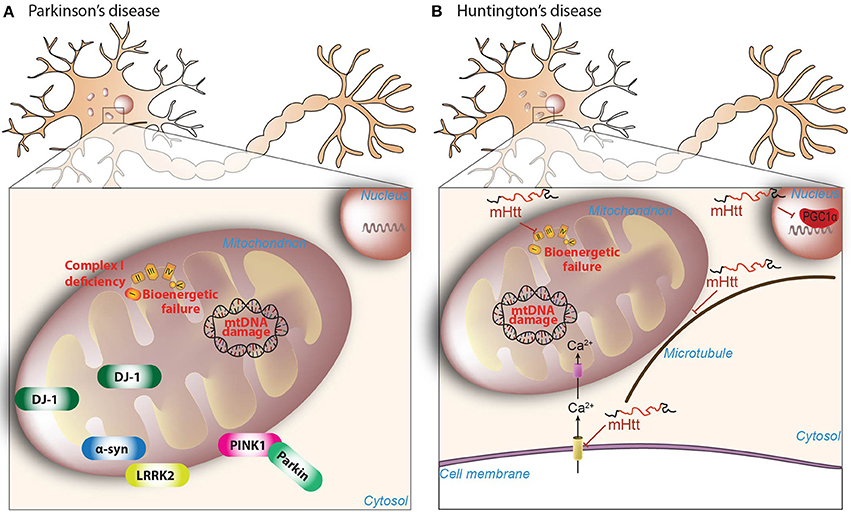
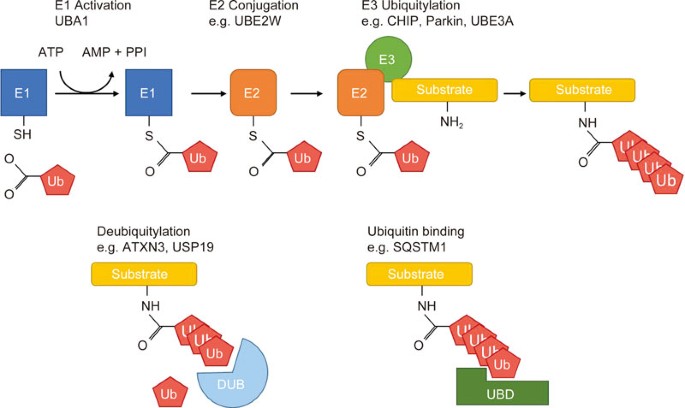
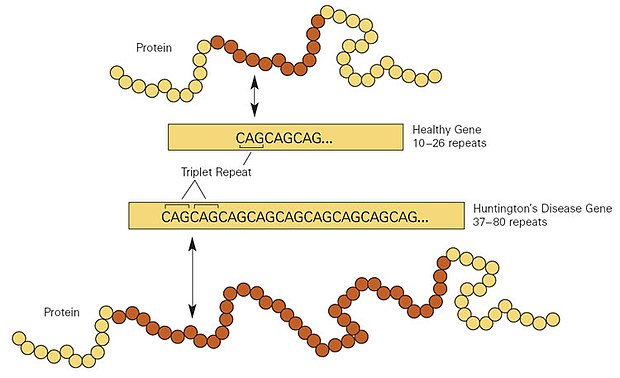
This disease is caused by expansion of the CAG repeats in exon 1 of the huntingtin which encodes Huntingtin protein Htt. Mitochondria as important organelles play crucial roles in the most of. What is Huntingtons disease.
Huntingtons disease is an incurable hereditary brain disorder that damages brain cells. About Huntingtons disease Huntingtons disease is an inherited condition that damages certain nerve cells in the brain.
Huntington disease is caused by gradual degeneration of parts of the basal ganglia called the caudate nucleus and putamen.
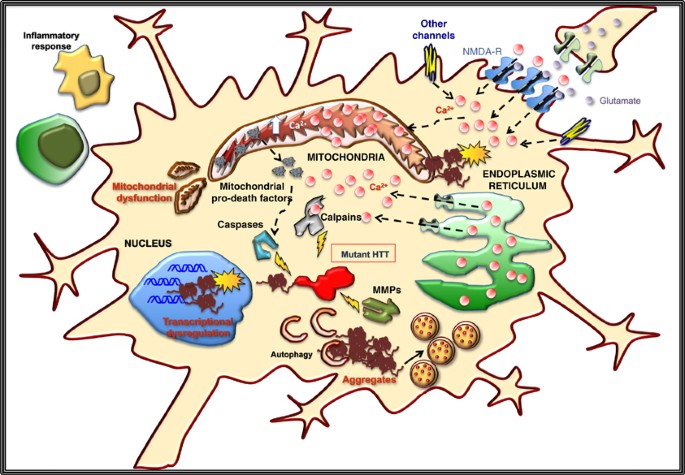
Mitochondria as important organelles play crucial roles in the most of. They help smooth out and coordinate movements. HD and the Brain Huntingtons disease is a neurodegenerative condition meaning that symptoms are caused by the death of nerve cells in the brain. Damage to the striatum over time is. Huntingtons Disease HD mainly affects nerve cells in the brain called medium spiny neurons MSNs. Various cellular and molecular events play role in the pathology of HD. Huntingtons disease is an incurable hereditary brain disorder that damages brain cells. Nationwide an estimated 30000 people have Huntingtons disease. Amyloid beta in Alzheimers huntingtin in Huntingtons disease SOD1 in ALS and alpha-synulcein in Parkinsons disease and other synucleinopathies 5.
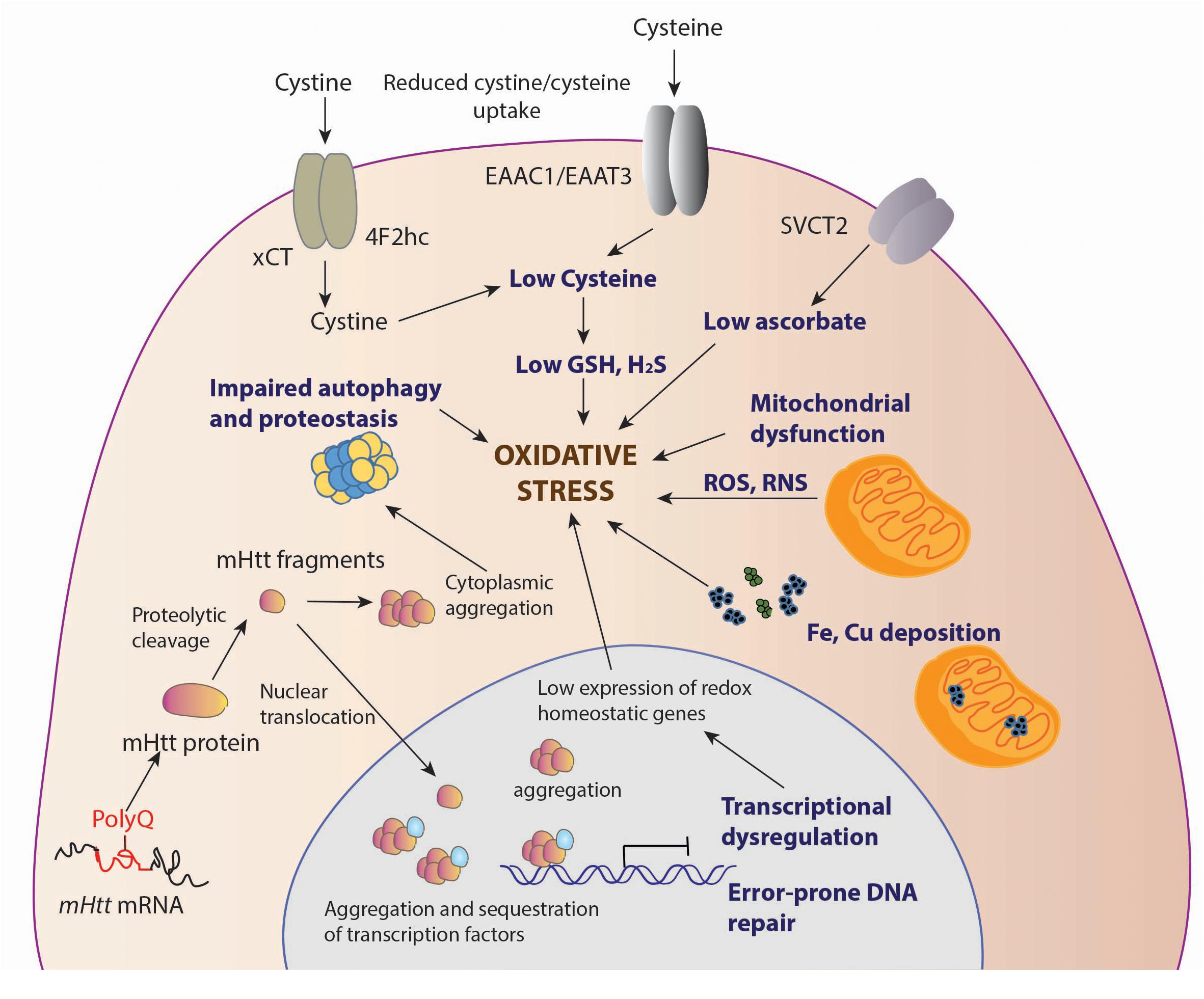
It is widely recognized that oxidative stress plays a role in many neurodegenerative diseases and increases as a byproduct of normal aging. MSNs receive and coordinate information from other neurons in the brain to control movement intellectual processes and emotion. Over many years this mutant huntingtin protein forms clumps in brain cells and causes them to become damaged and die. Various cellular and molecular events play role in the pathology of HD. Mitochondria as important organelles play crucial roles in the most of. An accumulation of DNA breakages is thought to contribute to the development of Huntingtons disease a devastating and currently incurable condition where brain cells slowly die. This disease is caused by expansion of the CAG repeats in exon 1 of the huntingtin which encodes Huntingtin protein Htt.




















Post a Comment for "What Cells Are Damaged In Huntington's Disease"